Audi tyre particulate filter passes endurance test
 The Audi Environmental Foundation and Technical University of Berlin have developed filters designed to prevent tyre wear particles and other substances from being washed into bodies of water (Photo: Audi)
The Audi Environmental Foundation and Technical University of Berlin have developed filters designed to prevent tyre wear particles and other substances from being washed into bodies of water (Photo: Audi)
The Audi Environmental Foundation has developed filters for urban runoff in conjunction with the Technical University of Berlin. They prevent tyre wear particles and other substances from being washed into sewers and bodies of water along with rainwater. Initial field and lab tests have now demonstrated the efficiency of the UrbanFilter project.
According to Audi, an estimated 110,000 metric tonnes of tyre and road wear particulate ends up on the streets in the form of microplastics every year in Germany alone. From there, it is blown into the environment by the wind, or is washed by the rain as urban runoff through the sewers into the soil and rivers – and ultimately the oceans. “Our goal is to take preventative actions wherever possible so that fewer microplastics get into the environment,” says Rüdiger Recknagel, Director of the Audi Environmental Foundation.
Together with the Technical University of Berlin (Department of Urban Water Management), the Audi Environmental Foundation is therefore developing an innovative new filter concept for urban runoff. These filters can be combined individually depending on the road and traffic situation. They trap the respective dirt particles as close as possible to the location where they are generated – before rainwater can rinse them into the sewers. The project was launched in September 2020.
Laboratory and real-life testing
Tests in a laboratory at TU Berlin have shown that the filters work very effectively. Without clogging up, the filters managed to permanently trap “genuine” street cleaning waste, cigarette filters, microplastics in the form of plastic granulates up to three millimetres in size, candy wrappers, and lids of disposable coffee cups. “The system does this not just when it’s drizzling, but also when it’s lashing rain,” says Daniel Venghaus, research associate in the Department of Urban Water Management at TU Berlin.
For more than a month now, a filter has also been deployed on a busy road in Berlin. The Urbanfilter successfully mastered its first stress test during a series of storms in mid-February. It is due to remain in service at its present location until the end of the year. The researchers want to take samples both of the intake and of the water draining away to determine its effectiveness in real-life operating conditions throughout the seasons. Furthermore, initial discussions are already underway with the ADAC Driving Safety Center in Berlin-Brandenburg to install filters on its routes to gain a better understanding of the filtering of wear particles in different driving situations.
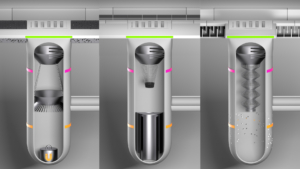
The sediment filters are divided into three zones – street, sewer, and drain – and consist of nine modules. Up to three modules can be combined to achieve the best result depending on the location. In the uppermost area (road), this might be a special runoff channel. Below this, in the sewer itself, larger solids are filtered out, for example, with the aid of an optimized leaf basket or what is known as a filter skirt. The lowest area (drain) is about fine filtration, for which a magnet module can be used.
(l to r)combination of side inlet grille and filter skirt and sedimentation module, in the middle: the combination of retention space in the curb, funnel and infiltration in the shaft, right: the combination of porous asphalt, optimized leaf basket and magnetic module (Photo: Audi)
Depending on the catchment area, different filters are required to filter the floating, suspended and sedimentable particles from the water. The filters contribute to a continuous improvement of the water quality and relieve rivers and lakes. Technically, both fine pore structures such as larger retention spaces, but also sieves of different mesh sizes, magnetic fields and the possibility of local infiltration in the modules are used. The service life and performance of the filters can be significantly increased by an intelligent networking concept that is additionally adapted to the filters, for example to optimize street cleaning.
This filtering out of ultra-fine particles is still presenting the team of researchers around Daniel Venghaus with challenges. “The system has already passed tests with ground tyre rubber between 20 to 1,000 micrometres (µm) in size in conditions of light to medium rainfall. Now we’re working on improving the filter performance when there is strong rainfall,” explains Venghaus. However, ground tyre rubber, which can be used for testing purposes, behaves differently to genuine tyre wear particles. Field tests on roads will provide further information.
The goal of the tests and of further development work is for the UrbanFilter to be in operation for up to a year without having to be maintained or cleaned. This is where intelligent connectivity comes into play. A lot of different information converges here, such as the street cleaning schedule, the traffic volume on the street, rush hour times, and the weather forecast. This even includes whether there are a lot of trees along the roadside or whether it is a popular area for dog walking. Based on these factors, it is possible to predict the contamination level of each individual filter and determine when the best time to empty it is. A filter could be emptied preventively, for example, before strong rains are due to fall.”


 BWR Motorsport
BWR Motorsport
Comments